Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

Medical tourism in India especially Nashik is a rapidly growing sector that attracts patients from around the world seeking affordable, high-quality medical care.
Nashik, known for its pilgrimage sites, is also developing as a medical tourism destination. The city offers a range of medical services with modern facilities and trained professionals. It’s becoming known for specialties such as orthopedics, cardiology, and cosmetic surgery.
Here are some key points about medical tourism in India, especially Nashik:
Affordability: Medical procedures in India can be significantly less expensive than in Western countries. This cost advantage extends to both the treatments and associated expenses like accommodation and travel.
Quality of Care: Many hospitals and clinics in Nashik are accredited by international organizations such as the Joint Commission International (JCI). These institutions often employ highly trained professionals and use advanced technology.
Specialized Treatments: India is known for its expertise in various fields, including cardiology, orthopedics, oncology, neurology, and cosmetic surgery. The country also has a strong tradition in alternative medicine, including Ayurveda and yoga.
Language and Communication: English is widely spoken in the medical community, which helps ease communication barriers for international patients.
Infrastructure: Nashik has state-of-the-art medical facilities and a range of accommodation options for patients and their families.
Legal and Ethical Considerations: Patients should research and choose accredited institutions and ensure that they understand the legal and ethical standards of the healthcare provider. It’s also important to be aware of the potential risks and ensure proper follow-up care.
Visa and Travel: Many countries offer medical visas for patients traveling to India for treatment. The process can vary, so it’s wise to check specific requirements before planning your trip.
Cultural Sensitivity: India is diverse, and patients might experience cultural differences. Many hospitals provide services to assist with these differences, such as translators and cultural liaison officers.
Medical tourism in India continues to grow due to these factors, making it an appealing option for those seeking both quality and cost-effective healthcare solutions.
Medical treatments available in Nashik:
Medical tourism in India covers a broad spectrum of specialties, with several areas being particularly popular due to their quality of care, affordability, and expertise. Here are some of the most sought-after medical treatments and specialties:
Bariatric Surgery:
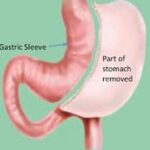
Weight loss surgeries such as gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy are frequently sought after. Major centers in Nashik offer these services. Bariatric surgery refers to a variety of surgical procedures aimed at helping people with severe obesity achieve significant weight loss. These surgeries generally work by altering the digestive system to limit food intake, reduce nutrient absorption, or both. The main types include:
Gastric Bypass (Roux-en-Y): This procedure creates a small stomach pouch and reroutes the intestines so that food bypasses a significant portion of the digestive tract.
Sleeve Gastrectomy: This involves removing a large portion of the stomach to create a small, sleeve-shaped stomach. It limits the amount of food you can eat and reduces hunger hormones.
Adjustable Gastric Banding (Lap-Band): This involves placing an adjustable band around the upper part of the stomach to create a small stomach pouch, which limits food intake.
Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD/DS): This combines a sleeve gastrectomy with a bypass of a large portion of the small intestine, reducing both food intake and nutrient absorption.
Bariatric surgery is usually considered for individuals with a Body Mass Index (BMI) of 40 or higher, or a BMI of 35 or higher with obesity-related health conditions. It often leads to significant weight loss and improvement in conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and sleep apnea, but it also requires lifelong changes in diet, exercise, and sometimes vitamin supplementation
Eye Care:
Treatments for cataracts, LASIK surgery, and other eye conditions are well-developed in India. Hospitals in Nashik are known for their advanced eye care facilities. Ophthalmological operations address various eye conditions and can be crucial for improving or preserving vision. Common procedures include:
YAG Laser Capsulotomy: Treats posterior capsule opacity (cloudy vision after cataract surgery) by using a laser to create an opening in the capsule behind the IOL.
Cataract Surgery: Removes the cloudy lens and replaces it with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL) to restore clear vision.
LASIK: A laser surgery that reshapes the cornea to correct refractive errors like nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism.
PRK (Photorefractive Keratectomy): Similar to LASIK, this laser surgery corrects vision but involves removing the corneal surface layer before reshaping.
Vitrectomy: Removes the vitreous gel from the eye to treat conditions like retinal detachment, diabetic retinopathy, or macular hole.
Glaucoma Surgery: Includes procedures like trabeculectomy or tube shunt surgery to lower intraocular pressure and manage glaucoma.
Retinal Detachment Surgery: Repairing a detached retina using techniques such as laser therapy, cryopexy (freezing), or scleral buckling.
Keratoplasty (Corneal Transplant): Replaces a damaged or diseased cornea with a donor cornea to restore vision.
Cardiac surgeries:

Heart surgeries, including bypass surgeries, angioplasties, and valve replacements, stenting, and cardiac surgery. Facilities may also offer diagnostics like echocardiography and stress tests. Major hospitals in Nashik have excellent cardiac departments. Cardiac surgeries are performed to treat various heart conditions and improve heart function. Key types include:
These surgeries aim to improve heart function, relieve symptoms, and enhance quality of life for patients with serious heart conditions.
Cosmetic and Plastic Surgery:
This includes procedures like rhinoplasty, liposuction, facelifts, and breast augmentation. Nashik has numerous well-regarded cosmetic surgery clinics. Cosmetic Surgery and Plastic Surgery are often used interchangeably, but they refer to different types of procedures with distinct goals. Here’s a breakdown of both:
Focuses on enhancing or improving the appearance of a person. It is generally elective, meaning people choose to have the surgery to change their physical appearance.
Common Procedures:
Facelift (Rhytidectomy): Reduces the appearance of facial wrinkles and sagging.
Rhinoplasty: Reshapes the nose.
Breast Augmentation: Enhances the size and shape of breasts.
Liposuction: Removes excess fat from specific areas of the body.
Botox Injections: Reduces the appearance of wrinkles by paralyzing muscles.
Understanding these differences can help patients make informed decisions about the type of surgery that best suits their needs.
Dental Care:
High-quality dental procedures, including implants, cosmetic dentistry, and orthodontics, are offered at competitive prices. Nashik is known for its dental clinics. Dental Treatment refers to a wide range of procedures and services aimed at maintaining oral health, treating dental issues, and enhancing the appearance of teeth and gums. These treatments can be broadly categorized into preventive, restorative, cosmetic, and orthodontic care.
Treats gum disease and other conditions affecting the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. Common Procedures: Scaling and Root Planing: Deep cleaning procedures to remove plaque and tartar below the gum line. Gum Surgery: Procedures like flap surgery or gum grafts to treat advanced gum disease.
Regular dental visits are crucial for early detection of dental issues, preventing serious problems, and maintaining overall oral health. Proper dental care includes daily brushing, flossing, and a balanced diet, alongside professional dental services.
Dermatology:
Specialized care for skin conditions, including cosmetic dermatology, laser treatments, and management of chronic skin diseases.
Endocrinology:
Management of hormonal disorders, including diabetes care and treatment for thyroid and adrenal gland disorders.
Gastroenterology:
Services for digestive system disorders, including endoscopic procedures, liver treatments, and management of gastrointestinal diseases.
Infertility Treatments:
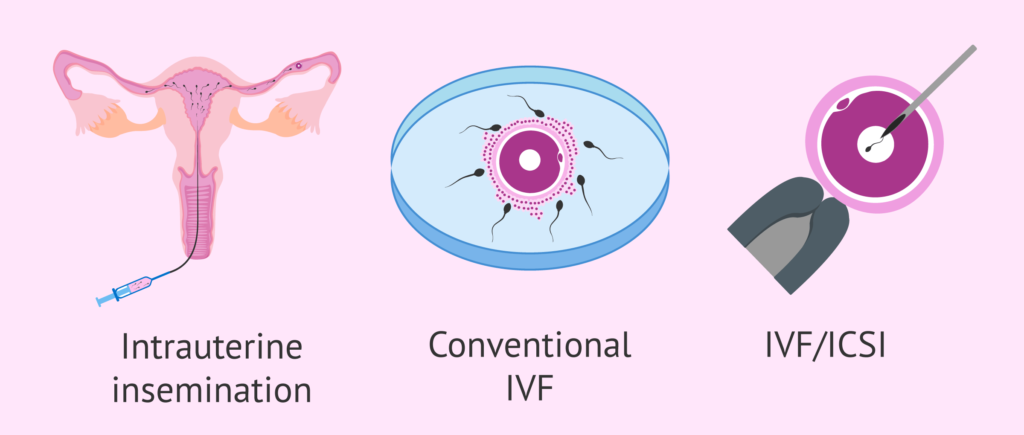
In vitro fertilization (IVF) and other assisted reproductive technologies are popular, with renowned fertility clinics in Nashik. Infertility Treatments encompass a variety of medical procedures and interventions aimed at helping individuals or couples conceive when they face challenges in getting pregnant. Infertility can be due to factors affecting either the male, the female, or both, and treatments are tailored based on the underlying cause(s) of infertility.
Types of Infertility Treatments:
1. Lifestyle Changes and Medication
Addresses health issues or lifestyle factors that may contribute to infertility. Common Interventions: Weight Management: Achieving a healthy weight can improve fertility. Diet and Nutrition: Ensuring proper nutrition and addressing deficiencies.
2. Ovulation Induction
Stimulates the ovaries to produce eggs in women who have irregular or absent ovulation.
3. Intrauterine Insemination (IUI)
Increases the chances of fertilization by placing sperm directly into the uterus. Sperm is collected, processed, and concentrated before being inserted into the uterus using a thin catheter. Often used in conjunction with ovulation-inducing medications to increase success rates.
4. In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
A highly effective treatment that involves fertilizing an egg outside the body and then implanting the resulting embryo into the uterus. Ovarian Stimulation: Hormones are used to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs. Egg Retrieval: Eggs are collected from the ovaries using a minor surgical procedure. Fertilization: Eggs are fertilized with sperm in a laboratory setting. Embryo Transfer: The resulting embryo(s) is transferred into the uterus for implantation.
IVF Variants:
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI): A single sperm is injected directly into an egg, often used for male infertility. Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT): Screening embryos for genetic conditions before transfer.
5. Assisted Hatching
Enhances the chances of an embryo implanting in the uterus during IVF. A small hole is made in the outer layer of the embryo (the zona pellucida) to assist in its implantation.
6. Egg or Sperm Donation
Used when a couple cannot use their own eggs or sperm due to medical conditions. Egg Donation: An egg from a donor is fertilized with the partner’s sperm and the embryo is transferred to the recipient’s uterus. Sperm Donation: Donor sperm is used in conjunction with IUI or IVF.
7. Surrogacy
Purpose: Involves another woman carrying and giving birth to a baby for the intended parents.
Types: Traditional Surrogacy: The surrogate’s egg is used, making her the biological mother. Gestational Surrogacy: The surrogate carries an embryo created via IVF, with no genetic connection to the child.
8. Surgery
Corrects structural problems in the reproductive organs that may cause infertility.
Laparoscopy: Used to treat endometriosis, remove fibroids, or repair blocked fallopian tubes. Hysteroscopy: Used to remove polyps, fibroids, or adhesions from the uterus.
9. Male Infertility Treatments
Addresses issues like low sperm count, poor sperm motility, or blockages.
Medication: Hormonal treatments or medications to improve sperm production. Surgery: Procedures like varicocelectomy to correct varicoceles, or surgery to remove blockages. Sperm Retrieval Techniques: Techniques like Testicular Sperm Extraction (TESE) for men with no sperm in their ejaculate.
Importance of Counseling and Support:
Infertility treatments can be emotionally and physically challenging. Counseling and psychological support are often recommended to help individuals and couples cope with the stress and emotional impact of fertility treatments.
Factors to Consider:
Age: Success rates of treatments like IVF decrease with age, especially after 35. Underlying Cause: Treatment effectiveness varies based on the specific infertility cause. Financial Costs: Fertility treatments can be expensive, and insurance coverage varies. Each case of infertility is unique, and a healthcare provider typically tailors the
Neurology and Neurosurgery:
Treatments for neurological disorders and brain surgeries are available at advanced facilities in Nashik. Neurology: Care for neurological disorders such as epilepsy, stroke, and multiple sclerosis. Treatments may include advanced diagnostic tools like MRI and CT scans. Neurosurgery: Surgical interventions for brain and spinal cord issues, including tumor removal and treatment of spinal disorders. Neurology and Neurosurgery Procedures involve the diagnosis, treatment, and management of disorders affecting the nervous system, which includes the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. While neurology primarily deals with non-surgical treatments, neurosurgery involves surgical interventions for more severe neurological conditions. Here’s an overview of various procedures in both fields:
Neurology Procedures:
1. Electroencephalogram (EEG)
Records electrical activity in the brain to diagnose conditions like epilepsy, sleep disorders, and brain tumors. Electrodes are placed on the scalp to detect brain wave patterns.
2. Electromyography (EMG) and Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS)
Assess the health of muscles and the nerve cells that control them, useful for diagnosing conditions like peripheral neuropathy, carpal tunnel syndrome, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
EMG involves inserting a needle electrode into the muscle to record electrical activity, while NCS uses surface electrodes to measure the speed and strength of signals traveling along nerves.
3. Lumbar Puncture (Spinal Tap)
Collect cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to diagnose conditions like meningitis, multiple sclerosis, and subarachnoid hemorrhage. A needle is inserted into the lower back to access the spinal canal and draw fluid.
4. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computed Tomography (CT) Scans
Imaging studies to visualize the brain and spinal cord, often used to diagnose strokes, tumors, and degenerative diseases.
MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves, while CT uses X-rays to create detailed images.
5. Carotid Ultrasound
Evaluates blood flow through the carotid arteries, which supply blood to the brain, to assess the risk of stroke. A non-invasive ultrasound probe is used to visualize the arteries and measure blood flow.
6. Evoked Potentials
Measures the electrical activity in the brain in response to stimuli, used to diagnose conditions like multiple sclerosis and optic neuritis. Electrodes are placed on the scalp to record brain responses to visual, auditory, or sensory stimuli.
7. Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) Programming
Adjusts the settings of implanted DBS devices used to treat Parkinson’s disease, essential tremor, and dystonia. Neurologists program the device to deliver electrical impulses that modulate abnormal brain activity.
Neurosurgery Procedures:
1. Craniotomy
Surgical removal of part of the skull to access the brain, commonly performed for brain tumors, aneurysms, and traumatic brain injuries. A section of the skull is temporarily removed, the necessary brain surgery is performed, and the skull is then replaced.
2. Spinal Fusion
Purpose: Stabilizes the spine by fusing two or more vertebrae together, often used to treat conditions like degenerative disc disease, scoliosis, and spinal fractures.
Procedure: Bone grafts, metal rods, or screws are used to fuse the vertebrae, preventing movement between them.
3. Microdiscectomy
Relieves pressure on a spinal nerve caused by a herniated disc, often resulting in significant pain relief. A minimally invasive surgery where a small portion of the herniated disc is removed.
4. Aneurysm Clipping or Coiling
Treats brain aneurysms to prevent rupture, which can lead to hemorrhagic stroke. Clipping: A small metal clip is placed at the base of the aneurysm to block blood flow. Coiling: A catheter is used to fill the aneurysm with tiny coils, inducing clotting and sealing it off.
5. Ventriculoperitoneal (VP) Shunt Placement
Treats hydrocephalus by diverting excess cerebrospinal fluid from the brain to the abdominal cavity. Procedure: A shunt system, including a catheter and valve, is surgically placed to drain the fluid.
6. Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS)
A non-invasive treatment for brain tumors, arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), and trigeminal neuralgia. Procedure: Focused radiation beams are delivered precisely to the target, minimizing damage to surrounding tissue.
7. Endovascular Coiling
Minimally invasive procedure to treat brain aneurysms and AVMs.
Procedure: A catheter is guided through the blood vessels to the aneurysm site, where coils or other devices are deployed to block blood flow and prevent rupture.
8. Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) Surgery
Treats movement disorders like Parkinson’s disease and dystonia by implanting electrodes in specific brain areas.
Procedure: Electrodes are surgically implanted in the brain, connected to a pulse generator placed under the skin of the chest.
9. Laminectomy
Relieves pressure on the spinal cord or nerves caused by spinal stenosis or herniated discs.
Procedure: The lamina (part of the vertebra) is removed to create more space for the spinal cord and nerves.
10. Carpal Tunnel Release
Procedure: The transverse carpal ligament is cut to reduce pressure on the nerve.
Importance of Neurological and Neurosurgical Care:
Timely diagnosis and treatment of neurological conditions are crucial to prevent complications, manage symptoms, and improve the patient’s quality of life. Neurosurgical interventions are often complex and require precise planning and execution, emphasizing the importance of specialized care.
Considerations for Neurology and Neurosurgery Treatments:
Patient-Specific Factors: Treatment plans are highly individualized, considering factors like age, overall health, and the specific neurological condition.
Risks and Benefits: Both neurological and neurosurgical treatments come with potential risks, so thorough discussions with healthcare providers are essential to make informed decisions.
Follow-up Care: Regular follow-up is critical to monitor the progress of treatment, manage any side effects, and adjust therapies as needed.
Neurology and neurosurgery play pivotal roles in managing and treating disorders that affect the nervous system, offering a range of interventions from medication to complex surgical procedures.
Obstetrics and Gynecology:

Specialized care in women’s health, including high-risk pregnancies, infertility treatments, and advanced gynecological surgeries. Obstetrics and Gynecology (OB-GYN) is a medical specialty that encompasses two main fields: obstetrics, which focuses on pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period, and gynecology, which deals with the health of the female reproductive system outside of pregnancy. OB-GYNs provide comprehensive care for women throughout their lives, addressing a wide range of health issues from adolescence through menopause and beyond.
1. Obstetric Treatments
a. Prenatal Care
To monitor and support the health of the mother and developing fetus during pregnancy.
Regular Check-ups: Routine examinations to track the progress of pregnancy, including weight, blood pressure, and fetal growth. Ultrasound Scans: Imaging to monitor fetal development, detect abnormalities, and determine the due date. Genetic Screening and Testing: Tests such as amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling (CVS) to identify genetic disorders. Nutritional and Lifestyle Counseling: Guidance on diet, exercise, and avoiding harmful substances.
b. Labor and Delivery
To manage and facilitate the process of childbirth, ensuring the safety of both mother and baby. Vaginal Delivery: Natural childbirth through the birth canal. Cesarean Section (C-Section): Surgical delivery of the baby through an incision in the abdomen and uterus. Epidural Anesthesia: Pain relief administered during labor. Assisted Vaginal Delivery: Use of tools like forceps or a vacuum extractor to aid in the delivery.
c. Postpartum Care
To support the mother’s recovery after childbirth and address any complications.
Physical Examinations: Assessing healing and recovery from delivery. Breastfeeding Support: Guidance and assistance with breastfeeding techniques and challenges. Mental Health Support: Screening and treatment for postpartum depression and anxiety.
d. High-Risk Pregnancy Management
To provide specialized care for pregnancies with increased risk of complications.
Common Conditions Managed: Gestational Diabetes, Pre-eclampsia and Eclampsia, Multiple Pregnancies (Twins, Triplets, etc.) Placenta Previa and Placental Abruption
e. Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART)
To help individuals and couples conceive when facing infertility issues. In Vitro Fertilization (IVF), Intrauterine Insemination (IUI), Egg and Sperm Donation, Surrogacy Arrangements
2. Gynecologic Treatments
a. Preventive Services
To maintain reproductive health and prevent diseases.
Pap Smears: Screening for cervical cancer, Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Vaccination: Prevention of HPV-related cancers. Breast Exams and Mammography: Screening for breast cancer. Bone Density Testing: Screening for osteoporosis, especially post-menopause.
b. Medical Treatments for Gynecologic Conditions
To manage and treat various conditions affecting the female reproductive system.
Common Conditions and Treatments: Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Hormonal treatments and lifestyle modifications. Endometriosis: Hormonal therapy, pain management, and fertility treatments. Menstrual Disorders: Medications to regulate menstrual cycles and manage heavy bleeding. Urinary Incontinence: Behavioral therapies and medications.
c. Surgical Procedures
To correct structural issues or remove diseased tissues within the reproductive system.
Hysterectomy: Removal of the uterus, sometimes including the cervix, ovaries, and fallopian tubes. Myomectomy: Removal of uterine fibroids while preserving the uterus. Laparoscopy and Laparotomy: Minimally invasive and open surgeries for various gynecologic conditions. Endometrial Ablation: Treatment for abnormal uterine bleeding by removing the uterine lining. Oophorectomy: Removal of one or both ovaries. Salpingectomy: Removal of one or both fallopian tubes.
d. Infertility Treatments
To assist individuals and couples in achieving pregnancy.
Common Treatments: Ovulation Induction: Medications to stimulate egg production. IVF and ICSI (Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection) Surgical Treatments: Correcting anatomical issues like blocked fallopian tubes or endometriosis.
e. Management of Menopause and Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
To alleviate symptoms associated with menopause and reduce the risk of osteoporosis.
Common Treatments: Estrogen and Progesterone Therapy. Non-Hormonal Medications: For managing hot flashes and other symptoms.
f. Sexual Health and Dysfunction Treatments
To address issues affecting sexual function and satisfaction.
Common Treatments: Vulvar and Vaginal Treatments: For conditions like vaginitis and vulvodynia. Pelvic Floor Therapy: To strengthen pelvic muscles. Medications and Counseling: For sexual dysfunction and psychological support.
g. Gynecologic Oncology
To diagnose and treat cancers of the female reproductive system.
Common Treatments: Surgery: Removal of cancerous tissues or organs. Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy. Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy
Family Planning and Contraception To help individuals and couples plan and manage pregnancies. Common Services: Contraceptive Counseling and Prescriptions: Pills, IUDs, implants, injections, etc. Permanent Sterilization: Tubal ligation or vasectomy (performed by urologists for males).
b. Pelvic Pain Management To diagnose and treat chronic pelvic pain.
Medications: Pain relievers, hormonal treatments. Physical Therapy. Surgical Interventions: For endometriosis, fibroids, or adhesions.
c. Reproductive Endocrinology
Common Treatments: Fertility Preservation: Egg or embryo freezing. Hormone Therapy: For disorders like thyroid dysfunction impacting fertility.
Regular visits to an OB-GYN are essential for maintaining reproductive health, early detection of potential issues, and managing conditions that can affect overall well-being. Preventive care, such as screenings and vaccinations, plays a crucial role in preventing serious health problems. Additionally, comprehensive obstetric care ensures healthy pregnancies and safe deliveries, while gynecologic care addresses a wide range of health issues that can impact a woman’s quality of life.
Common Procedures in Obstetrics and Gynecology:
a. Diagnostic Procedures
Pelvic Exam: Physical examination of the female reproductive organs. Transvaginal Ultrasound: Imaging to evaluate the uterus, ovaries, and other pelvic structures. Hysteroscopy: Insertion of a scope into the uterus to diagnose and treat abnormalities. Laparoscopy: Minimally invasive surgery to examine the abdominal and pelvic organs.
b. Therapeutic Procedures
Dilation and Curettage (D&C): Removal of tissue from the inside of the uterus, often after a miscarriage or for abnormal bleeding. Colposcopy: Detailed examination of the cervix, vagina, and vulva for signs of disease. Biopsy Procedures: Removal of tissue samples for laboratory analysis to diagnose cancers and other conditions.
Oncology:

Cancer treatments, including chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and surgical interventions. Some hospitals might have specialized cancer centers in Nashik and offer comprehensive cancer care.
Orthopedic Surgery:
This includes joint replacements, spinal surgeries, and other musculoskeletal, bone and joint issues, including arthroscopic surgery, and treatment for sports injuries. Hospitals in Nashik are well-known for their advanced orthopedic care. Orthopedic Surgery involves the surgical treatment of conditions affecting the musculoskeletal system, which includes bones, joints, ligaments, tendons, muscles, and nerves. Orthopedic surgeons address a wide range of issues, from acute injuries like fractures to chronic conditions such as arthritis. The goal is to restore function, alleviate pain, and improve the quality of life for patients.
Types of Orthopedic Surgeries:
Joint Replacement Surgery (Arthroplasty)
Total Hip Replacement (THR): Replacement of the hip joint with an artificial socket and ball.
Total Knee Replacement (TKR): Replacement of the knee joint with metal and plastic components.
Shoulder Replacement: Replacement of the shoulder joint, which can be a total or partial replacement.
Partial Joint Replacement: Only the damaged part of the joint is replaced, often used in knee or hip surgeries.
Arthroscopy
Meniscus Repair: Repair of a torn meniscus in the knee. Ligament Reconstruction: Reconstructing torn ligaments, such as the ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) in the knee. Rotator Cuff Repair: Repairing torn tendons in the shoulder. Removal of Loose Bodies: Removing fragments of bone or cartilage from the joint.
Fracture Repair
Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF): Realigning the bone fragments and securing them with metal plates, screws, or rods. External Fixation: Using an external frame to stabilize the bone while it heals, typically used in severe fractures. Intramedullary Nailing: Inserting a metal rod into the marrow canal of a long bone, such as the femur or tibia, to stabilize the fracture.
Spinal Surgery
Purpose: To treat conditions affecting the spine, such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, scoliosis, or spinal fractures.
Common Procedures:
Spinal Fusion: Joining two or more vertebrae together to stabilize the spine and relieve pain. Discectomy: Removal of a herniated or damaged disc that is pressing on a nerve. Laminectomy: Removal of part of the vertebra (lamina) to relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerves.
Pulmonology:
Care for respiratory conditions such as asthma, COPD, and sleep apnea. Treatments may include advanced diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. Pulmonology is a medical specialty focused on the diagnosis and treatment of diseases and conditions affecting the respiratory system, including the lungs, airways, and respiratory muscles. Pulmonologists manage a wide range of acute and chronic respiratory conditions, providing both non-surgical and surgical treatments to improve breathing, manage symptoms, and enhance the quality of life for patients.
1. Diagnostic Procedures
Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs): To assess lung function, including the capacity and flow of air, as well as gas exchange efficiency. Common Tests: Spirometry: Measures the amount and speed of air that can be inhaled and exhaled. Lung Volume Measurement: Determines the total capacity of the lungs. Diffusion Capacity Test: Assesses how well oxygen moves from the lungs to the blood.
Bronchoscopy: To visualize the inside of the airways and lungs, collect tissue samples, and remove blockages. Procedure: A thin, flexible tube with a camera (bronchoscope) is inserted through the nose or mouth into the lungs.
Imaging Studies: Chest X-ray: Detects abnormalities like infections, tumors, and fluid accumulation. Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: Provides detailed images of the lungs, often used to diagnose conditions like lung cancer, pulmonary embolism, and interstitial lung disease. Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scan: Used in cancer diagnosis to detect malignant lung tumors and assess their spread.
Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) Analysis: Measures the levels of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and acidity (pH) in the blood to assess respiratory function. A blood sample is taken from an artery, usually in the wrist, for analysis.
Sleep Studies (Polysomnography): To diagnose sleep-related breathing disorders, such as obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Monitors various physiological parameters during sleep, including breathing patterns, oxygen levels, heart rate, and brain activity.
2. Medical Treatments for Pulmonary Conditions
Immunotherapy: To treat allergic asthma or other allergy-related respiratory conditions by desensitizing the immune system to specific allergens. Procedure: Administered through injections (allergy shots) or sublingual tablets/drops over a period of time.
Pulmonary Rehabilitation: To improve lung function, increase physical fitness, and enhance the quality of life for patients with chronic respiratory diseases. Exercise Training: Tailored exercise programs to strengthen respiratory muscles and improve overall fitness. Education: Information on managing symptoms, using medications correctly, and making lifestyle changes. Breathing Techniques: Training in specific techniques like pursed-lip breathing to improve oxygen intake.
3. Interventional Pulmonology Procedures
Thoracentesis: To remove excess fluid from the pleural space (around the lungs) to relieve symptoms and diagnose the cause. A needle is inserted into the chest wall to drain fluid, which can then be analyzed for signs of infection, cancer, or other conditions.
Pleurodesis: To prevent the recurrence of pleural effusion (fluid accumulation) or pneumothorax (collapsed lung). A chemical irritant or talc is introduced into the pleural space, causing the lung to adhere to the chest wall, which eliminates the space where fluid or air could accumulate.
Endobronchial Ultrasound (EBUS): To diagnose lung cancer, infections, and other diseases causing enlarged lymph nodes in the chest. Combines bronchoscopy with ultrasound to visualize and biopsy lymph nodes or other structures within the chest.
Lung Biopsy: To diagnose lung conditions such as cancer, sarcoidosis, or interstitial lung disease by analyzing a sample of lung tissue. Tissue is collected via bronchoscopy, needle biopsy, or surgical methods. Airway Stenting: To keep the airways open in patients with obstructions caused by tumors, strictures, or external compression. A stent (a small tube) is placed in the airway using bronchoscopy.
4. Surgical Treatments
Lung Resection Surgery: To remove diseased or damaged portions of the lung, often performed for lung cancer or severe emphysema. Lobectomy: Removal of an entire lobe of the lung. Segmentectomy: Removal of a segment of a lobe. Pneumonectomy: Removal of an entire lung, typically used in more advanced lung cancer cases.
Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS): Minimally invasive surgical technique used for lung biopsy, removal of lung nodules, or treatment of pleural conditions. Small incisions are made in the chest, and a thoracoscope (a small camera) along with surgical instruments are used to perform the surgery.
Lung Transplantation: To replace a diseased lung with a healthy lung from a donor in patients with end-stage lung disease.Can involve a single lung, double lung, or heart-lung transplant, depending on the patient’s condition.
5. Management of Chronic Pulmonary Conditions
Asthma Management : To control asthma symptoms, reduce the frequency and severity of attacks, and improve lung function. Long-term Control Medications: Inhaled corticosteroids, long-acting bronchodilators. Quick-relief Medications: Short-acting bronchodilators (rescue inhalers). Action Plans: Personalized plans to manage asthma triggers and handle acute symptoms.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Management: To slow the progression of the disease, manage symptoms, and improve quality of life. Bronchodilators and Steroids: To open airways and reduce inflammation. Pulmonary Rehabilitation Oxygen Therapy Vaccinations: To prevent respiratory infections like influenza and pneumonia, which can exacerbate COPD.
Cystic Fibrosis Management : To manage the chronic lung infections and mucus buildup characteristic of cystic fibrosis. Airway Clearance Techniques: To help clear mucus from the lungs. Inhaled Medications: Antibiotics, bronchodilators, and mucolytics. Nutritional Support: To address the digestive issues associated with cystic fibrosis.
Importance of Pulmonology Care:
Pulmonology care is crucial for managing both acute and chronic respiratory conditions, improving breathing, and enhancing overall health and quality of life. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for preventing complications, slowing disease progression, and reducing the impact of respiratory disorders on daily life.
Individualized Care: Treatment plans are tailored to the specific condition, severity, and overall health of the patient. Lifestyle Factors: Smoking cessation, weight management, and environmental factors play a significant role in the management of many respiratory conditions. Regular Monitoring: Ongoing evaluation of lung function and symptoms is crucial to adjust treatments as needed and ensure optimal outcomes. Multidisciplinary Approach: Pulmonology often involves collaboration with other specialists, such as cardiologists, oncologists, and immunologists, to provide comprehensive care.
Rheumatology:
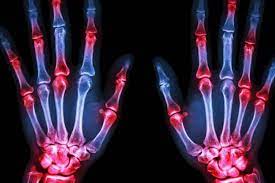
Treatment for autoimmune diseases and chronic inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus. Rheumatology Treatment involves the diagnosis and management of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases that affect the joints, muscles, and bones. Rheumatologists treat conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, gout, and other systemic autoimmune diseases. The goal of treatment is to relieve symptoms, improve quality of life, and prevent disease progression.
Types of Rheumatology Treatments:
Physical Therapy
Exercise Programs: Tailored routines to improve joint flexibility, strength, and endurance. Hydrotherapy: Exercise in warm water to reduce joint stress and pain. Manual Therapy: Hands-on techniques to improve joint mobility and reduce pain. Pain Relief Modalities: Use of heat, cold, ultrasound, or electrical stimulation to reduce pain and inflammation.
Common Techniques:
Joint Protection Techniques: Strategies to reduce strain on joints during daily activities. Adaptive Devices: Tools and devices that assist in performing tasks with less pain or difficulty. Ergonomic Advice: Recommendations on workplace or home modifications to ease joint stress.
Lifestyle Modifications
Common Recommendations: Diet: Anti-inflammatory diets rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids. Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce stress on joints. Exercise: Regular, low-impact physical activity like walking, swimming, or cycling. Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking to reduce inflammation and improve treatment outcomes.
Surgery
Common Surgical Procedures: Joint Replacement (Arthroplasty): Replacement of damaged joints with artificial ones, commonly done for hips and knees. Synovectomy: Removal of the inflamed synovial tissue that lines the joint. Tendon Repair: Surgery to repair or replace tendons damaged by inflammatory arthritis. Joint Fusion (Arthrodesis): Fusing bones together to stabilize or reduce pain in a joint.
Patient Education and Self-Management
Disease Education: Understanding the disease process and treatment options. Pain Management Techniques: Methods such as relaxation techniques, mindfulness, and stress management. Support Groups: Participation in support groups to share experiences and gain emotional support.
Importance of Early and Ongoing Treatment:
Rheumatic diseases are often chronic and progressive, meaning early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent joint damage, organ involvement, and disability. Ongoing treatment and regular monitoring by a rheumatologist are essential to adjust therapies as needed and manage the disease effectively.
Considerations for Rheumatology Treatments:
Personalized Treatment Plans: Treatment is tailored to the individual’s specific condition, severity, and overall health.
Monitoring and Side Effects: Many rheumatologic medications require regular monitoring to manage potential side effects and ensure effectiveness.
Comorbidities: Rheumatic diseases often coexist with other conditions like cardiovascular disease or osteoporosis, which may require integrated care.
Each patient’s journey with a rheumatic condition is unique, and treatment plans are designed to address the specific needs and challenges they face.
Urology:
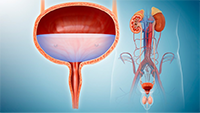
Treatment for urinary tract and male reproductive system issues, including minimally invasive surgeries and management of kidney stones. Urology Treatment refers to medical care and procedures that address disorders of the urinary tract and male reproductive organs. Urology covers a wide range of conditions, from urinary tract infections (UTIs) to more complex issues like kidney stones, bladder problems, and prostate diseases. Urologists also treat male infertility and sexual dysfunction. Here’s an overview of the various types of urology treatments:
Purpose: Restore sexual function in men who have difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection.
Regular check-ups with a urologist can help in the early detection and treatment of urological conditions, which can prevent complications and improve quality of life. Issues like prostate health, kidney function, and urinary tract health are critical to overall well-being, especially as individuals age.
Each patient’s situation is unique, and a urologist will typically customize a treatment plan to address the specific condition and individual needs.
Approximate cost of surgery in Nashik
The cost of surgery in Nashik can vary widely depending on the type of surgery, the complexity of the procedure, and the specific hospital or clinic. However, Nashik is known for offering relatively affordable medical care compared to major metropolitan areas like Mumbai or Delhi. Here’s a rough estimate of costs for various types of surgeries in Nashik:
Orthopedic Surgery:
Knee Replacement: ₹2,00,000 – ₹3,50,000
Hip Replacement: ₹2,50,000 – ₹4,00,000
Spinal Surgery: ₹1,50,000 – ₹3,00,000
Cardiac Surgery:
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): ₹2,00,000 – ₹4,00,000
Angioplasty: ₹1,00,000 – ₹2,00,000
Valve Replacement: ₹3,00,000 – ₹5,00,000
Cosmetic Surgery:
Rhinoplasty: ₹50,000 – ₹1,50,000
Liposuction: ₹60,000 – ₹1,50,000
Breast Augmentation: ₹1,00,000 – ₹2,50,000
Bariatric Surgery:
Gastric Bypass: ₹2,50,000 – ₹4,00,000
Sleeve Gastrectomy: ₹2,00,000 – ₹3,50,000
Infertility Treatments:
IVF: ₹1,00,000 – ₹2,50,000 per cycle
Eye Surgery:
LASIK Surgery: ₹30,000 – ₹60,000 per eye
Cataract Surgery: ₹20,000 – ₹50,000 per eye
Dental Surgery:
Dental Implants: ₹30,000 – ₹60,000 per implant
Root Canal Treatment: ₹5,000 – ₹15,000 per tooth
These costs are approximate and can vary based on the specific hospital or clinic, the surgeon’s expertise, and the patient’s individual needs. Additionally, many hospitals offer packages that include pre-surgery tests, post-surgery care, and follow-up consultations.
It’s advisable to consult with hospitals or medical centers in Nashik directly for precise quotes and to understand what each package includes.